In the modern manufacturing production, welding is one of the most important process methods, it is widely used in machinery manufacturing, nuclear industry, petrochemical industry, aerospace and many other fields. Because welding as an industrial "tailor", is a very important processing means in industrial production, at the same time, due to the existence of welding smoke, arc, metal splash, welding working environment is very bad, the quality of welding has a decisive impact on product quality.

With the development of industrial robots, sensors and artificial intelligence technologies, industrial welding robots gradually liberate workers from complex, harsh and even dangerous welding operation sites. According to the information released in IFR 2021, the number of industrial robots operating in factories around the world has reached a record 3 million, up 10% year on year. According to IFR 2018 data, 40% of industrial robots are used in the welding and cutting industry.
Welding robot from its birth to now, roughly experienced three generations: the first generation is the "teaching-reproduction" (Teaching and playing) working mode of the robot, due to the simple operation, do not need the environment model, teaching can correct the error caused by the mechanical structure and other characteristics, has been widely used in industrial welding production. The second generation is based on the structural environment and the offline programming type (Off-line programming) welding robot, Combine the obtained welding environment information and the CAD / CAM data of the workpiece, Using computer graphics techniques, Off-line planning and 3 D dynamic simulation of welding tasks, This kind of welding robot generally appears in the form of "industrial robot + offline programming" workstation, For example, the common third-party offline programming software RobotMaster, Sprutcam, RobotSmart on the market and the offline software RobotStudio, Roboguide of robot ontology manufacturers, etc. The third generation refers to an intelligent (Intelligent) welding robot equipped with a variety of sensors that can program and plan independently according to the welding environment after receiving operation instructions. Due to the complexity of its technology and the lag of artificial intelligence, this generation of welding robots is in the experimental research stage. At present, a few manufacturers at home and abroad have related products. The author calls the second generation of offline programming software called model-driven robot programming, and the third generation of model-driven automatic programming based on vision.

The following content is dry goods, which the view from the author personally, not completely represent the min Yue technology official. In the production process of the factory, welding and cutting have high reliability and process requirements. Pure visual-based cutting and welding schemes are suitable for academic research, but the current industrial site is not applicable to or only applicable to a specific subdivision scene. The reasons are shown below. First, after collecting the environment (workpiece) data, the welding robot needs to judge and calculate the welding or cutting position of the workpiece) data, which is a problem similar to LEVEL 4 autonomous driving technology. The difficulties include: 1. The collected data is missing or not accurate enough; 2. Even if the data meets the requirements, how to automatically and reliably extract the weld from the complex spot cloud data or image data; 3. Extract the processing track and how to determine the welding and cutting process, which is more difficult than the previous two points.
The third generation and the fourth generation of exam-free teaching program comparison
| scheme | Model-free drive | Based on model-driven and vision |
| Robotic trajectory planning method | Robot planning is realized by using the data environment detected by the sensors and combining with the robot kinematics algorithm. | Using the robot, workstation and workpiece model, according to the welding position in the workpiece model, combined with the robot kinematics algorithm. |
| Whether considered participation is required before production | Manual instruction or visual scanning procedures is required | The trajectory to be processed needs to be marked from the work piece number module in advance |
| intervene;interpose;meddle | Select the track to be processed from the scanning point cloud or automatically calculate according to the preset rules. | No intervention |
| Full perspective data | need | non-essential |
| precise localization | need | need |
| reliability | general | strong |
| universal property | No generality | strong |
In this case, the sensitive technology use in CAD / CAM, robotics and 3D vision, artificial intelligence, years of accumulation, in the existing mature robot intelligent programming software and 3D visual sensor, on the basis of the second and the third generation of two programming advantages, put forward the fourth generation free teaching automatic programming method-namely based on model drive and visual sensor autonomous programming.

As shown in the figure above, before production, the robot trajectory is used to plan for the work piece number module. Determine the corresponding process of each part through model annotation and automatic extraction. However, there are differences between digital offline software and actual workstation, including model and actual workpiece deviation, and deformation during welding and cutting process. For this problem, 3 D vision sensors of different scales are used for coarse and fine positioning of the trajectories. Through the combination of different sensors, the requirements of a large range of programming (more than 100mm) and high precision (less than 0.1mm) trajectory compensation can be met. The scheme is highly universal, there is no human intervention in the production process, and the combination of digital analog and sensor measured data improves the reliability.
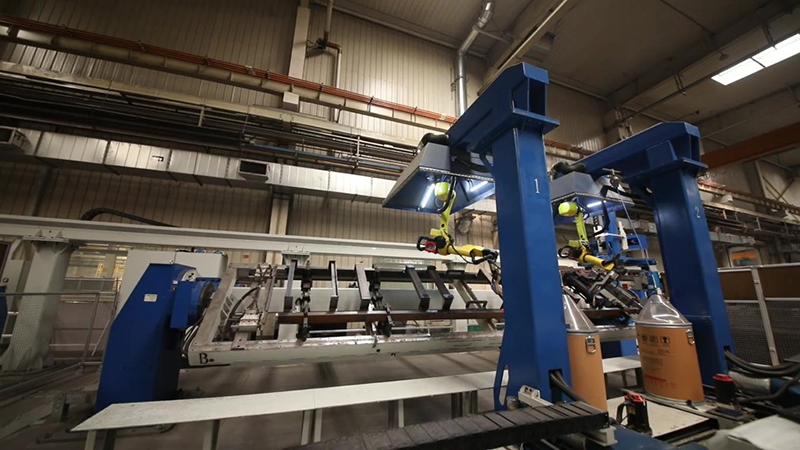
The operation of the offline programming software RobotSmart is described in detail below. Take the free teaching welding of the front vertical beam of a low-speed electric tricycle component as an example to explain the operation process.
Step 1, open the software and enter the welding module. According to the workpiece, the selection is to use the first sweep before welding, location, or tracking. The second step is to select the workpiece and welding edge for trajectory planning and automatic process calculation.
It is worth mentioning that at present, RobotSmart supports four family robots and broad robots. The line laser sensor only supports HA, WR and LDW models of Minyue Technology, and supports binocular structure light including SmartEye Vision WR yue self-developed R / HA series.